NVIDIA NIM
Accelerate Your AI Deployment With NVIDIA NIM Microservices
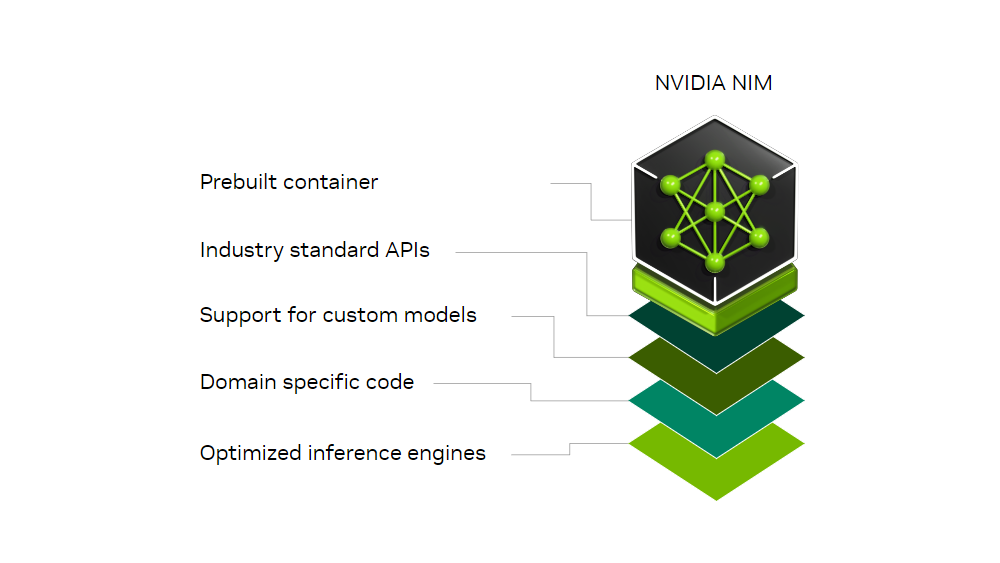
Part of NVIDIA AI Enterprise, NVIDIA NIM microservices are a set of easy-to-use microservices for accelerating the deployment of foundation models on any cloud or data center and helps keep your data secure. NIM microservices have production-grade runtimes including on-going security updates. Run your business applications with stable APIs backed by enterprise-grade support.
NVIDIA NIM microservices are designed to bridge the gap between the complex world of AI development and the operational needs of enterprise environments, enabling 10-100X more enterprise application developers to contribute to AI transformations of their companies.
NVIDIA NIM Agent Blueprints are reference examples that include pre-trained AI models and microservices that simplify the development of AI applications, providing a foundation for real-world use cases.
Create a digital human for customer service that combines NVIDIA NIM, ACE Microservices, Omniverse RTX rendering, and NeMo Retriever.
Rapidly ingest massive volumes of PDF documents. Extract text, graphs, charts, and tables for highly accurate retrieval.
The NVIDIA NIM Agent Blueprints for generative virtual screening shows how generative AI and accelerated NIM microservices can be used to design optimized small molecules smarter and faster.
Latest Releases
A widely used model for predicting the 3D structures of proteins from their amino acid sequences.
AlphaFold2 is a protein structure prediction model from Google DeepMind. AlphaFold2 demonstrates state-of-the-art performance at predicting protein structure form amino acid sequence, besting all other submissions on the Critical Assessment of protein Structure Prediction (CASP).
MolMIM is a transformer-based model developed by NVIDIA for controlled small molecule generation. MolMIM optimizes and samples molecules from the latent space guided by user-defined scoring functions, including functions from other models and functions based on experimental data testing for various chemical and biological properties. MolMIM can be deployed in the cloud or on-prem for enterprise-grade inference in computational drug discovery workflows, including virtual screening, lead optimization, and other lab-in-the-loop approaches.
ProteinMPNN (Protein Message Passing Neural Network) is a deep learning-based graph neural network designed to predict amino acid sequences for given protein backbones. This network leverages evolutionary, functional, and structural information to generate sequences that are likely to fold into the desired 3D structures.
RFdiffusion (RoseTTAFold Diffusion) is a powerful deep learning model designed to generate novel protein structures and complexes.
The NVIDIA DiffDock NIM is built for high-performance, scalable molecular docking at enterprise scale. It requires protein and molecule 3D structures as input but does not require any information about a binding pocket. Driven by a generative AI model and accelerated 3D equivariant graph neural networks, DiffDock predicts up to 7.6X more poses per second compared to the baseline published model, reducing the cost of computational drug discovery workflows, including virtual screening and lead optimization.
Latest Releases
Correction Diffusion (CorrDiff) is a generative AI model that downscales surface and atmospheric variables to improve the accuracy and resolution of weather data. CorrDiff is a two-step approach where the mean machine learning model is corrected by another diffusion model. CorrDiff exhibits skillful deterministic and probabilistic predictions and faithfully recovers spectra and distributions for extremes.
FourCastNet (FCN) NIM predicts accurate short to medium-range global predictions at a time-step size of 6 hours with predictive stability for over a year of simulated time (1,460 steps), while retaining physically plausible dynamics. The multivariant forecast includes surface and atmospheric variables such as wind speed, temperature and pressure at various vertical levels.
Latest Release
NIM for LLMs makes it easy for IT and DevOps teams to self-host large language models (LLMs) in their own managed environments while still providing developers with industry standard APIs that enable them to build powerful copilots, chatbots, and AI assistants that can transform their business.
Resources
This document provides insights into how to benchmark deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs), popular metrics and parameters, as well as a step-by-step guide.
Previous Releases
NIM for LLMs makes it easy for IT and DevOps teams to self-host large language models (LLMs) in their own managed environments while still providing developers with industry standard APIs that enable them to build powerful copilots, chatbots, and AI assistants that can transform their business.
NIM for LLMs makes it easy for IT and DevOps teams to self-host large language models (LLMs) in their own managed environments while still providing developers with industry standard APIs that enable them to build powerful copilots, chatbots, and AI assistants that can transform their business.
NIM for LLMs makes it easy for IT and DevOps teams to self-host large language models (LLMs) in their own managed environments while still providing developers with industry standard APIs that enable them to build powerful copilots, chatbots, and AI assistants that can transform their business.
Latest Releases
The Maxine eye contact model estimates the gaze direction of the input eye gaze and synthesizes a redirected gaze using a region of interest around one’s eyes known as an eye patch.
Latest Releases
NVIDIA NeMo™ Retriever text embedding NIM microservice bring the power of state-of-the-art text embedding models to your applications, offering unparalleled natural language processing and understanding capabilities. You can use NeMo Retriever embedding NIM microservices for semantic search, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), or any application that uses text embeddings. NeMo Retriever text embedding NIM microservices are built on the NVIDIA software platform, incorporating NVIDIA® CUDA®, TensorRT™, and Triton™ Inference Server to offer out-of-the-box GPU acceleration.
NVIDIA NeMo™ Retriever text reranking NIM microservice reorder citations by how well they match a query. This is a key step in the retrieval process, especially when the retrieval pipeline involves citations from different datastores that each have their own algorithms for measuring similarity.
Resources
Enterprises are sitting on a goldmine of data waiting to be used to improve efficiency, save money, and ultimately enable higher productivity. With generative AI, developers can build and deploy an agentic flow or a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) chatbot, while ensuring the insights provided are based on the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Generative AI applications have little, or sometimes negative, value without accuracy — and accuracy is rooted in data.
To help developers efficiently fetch the best proprietary data to generate knowledgeable responses for their AI applications, NVIDIA today announced four new NVIDIA NeMo Retriever NIM inference microservices.
To help developers efficiently fetch the best proprietary data to generate knowledgeable responses for their AI applications, NVIDIA today announced four new NVIDIA NeMo Retriever NIM inference microservices.
Employing retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is an effective strategy for ensuring large language model (LLM) responses are up-to-date and not hallucinated.
While various retrieval strategies can improve the recall of documents for generation, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. The retrieval pipeline depends on your data, from hyperparameters like the chunk size, and number of documents returned, to retrieval algorithms like semantic search or graph retrieval.
While various retrieval strategies can improve the recall of documents for generation, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. The retrieval pipeline depends on your data, from hyperparameters like the chunk size, and number of documents returned, to retrieval algorithms like semantic search or graph retrieval.
Businesses seeking to harness the power of AI need customized models tailored to their specific industry needs.
NVIDIA AI Foundry is a service that enables enterprises to use data, accelerated computing and software tools to create and deploy custom models that can supercharge their generative AI initiatives.
NVIDIA AI Foundry is a service that enables enterprises to use data, accelerated computing and software tools to create and deploy custom models that can supercharge their generative AI initiatives.
Latest Releases
NVIDIA NIM for NV-CLIP foundation model for image and text embedding generation.
Latest Releases
NVIDIA Riva automatic speech recognition (ASR) NIM microservices provide record-setting English language transcriptions. They deliver exceptional accuracy and robustness, adeptly handling diverse speech patterns and noise levels. They enable businesses to advance their voice-based services, ensuring superior user experiences.
NVIDIA Riva Megatron neural machine translation (NMT) NIM provides accurate real-time translation by leveraging extensive training on publicly available datasets featuring millions of parallel sentences. This cutting-edge translation NIM enables organizations to seamlessly integrate multilingual translation into their generative AI pipelines, broadening their global reach, engaging diverse audiences, and enhancing international collaboration.
NVIDIA Riva text-to-speech (TTS) NIM microservices integrate FastPitch and HiFiGAN models to generate high-fidelity speech from text. They enable businesses to create natural-sounding voices, elevating user engagement and delivering immersive experiences, setting a new standard in voice quality.
NVIDIA NIM Operator enables cluster administrators to operate and manage the lifecycle of the software components and services that are necessary to run LLM, embedding, and other NIM microservices and models in Kubernetes.
NVIDIA NIM, part of the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software platform available on the Google Cloud Marketplace, is a set of easy-to-use microservices designed for secure, reliable deployment of high performance AI model inferencing, is now integrated with Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), a managed Kubernetes service that is used to deploy and operate containerized applications at scale using Google’s infrastructure. NIM on GKE streamlines the deployment and management of AI inference workloads. It leverages the robust capabilities of GKE and NVIDIA's full stack AI platform on Google Cloud to deliver a powerful and flexible solution for AI model inferencing.